A talk with the company who brings you the computer game Civilization: Call To Power.
The sound of marching soldiers thunders through the cobbled streets as citizens bask in the glory of their triumphant leaders. No, this isn’t a post-election day Republican fantasy, it is just one of many scenes from the animated movies which introduce you to the first award-winning, top-selling computer game to be ported and run natively under Linux—Civilization: Call To Power.
Civilization: Call To Power is the latest in a series of games based on the original Civilization game. Civilization I hit the streets in 1991 and was an instant classic. In 1996 the sequel, Civilization II, won PC Gamer’s Game of the Year award and was named the “Strategy Game of All Time”. Together, Civilization I and II have sold over 2,500,000 copies, in an industry where a “hit” has to sell only 100,000 copies. Since its release in April, and up to the time of this writing, Civilization: Call To Power for Windows has been the number one selling PC game.

Figure 1.
This latest incarnation of the popular game was originally developed by Activision for MS Windows-based systems. The native X11 port to Linux was performed by Loki Entertainment Software, a relatively new company, started in 1998, devoted to porting the most popular PC games to Linux. As Scott Draeker (pictured at left below), President and Founder of Loki, says,
One way to put this success in perspective is to compare the PC game industry with the movie industry—both gross about $5 billion a year. Getting the rights to Civilization: Call To Power is like getting the rights to the next Star Wars sequel.
I talked with Scott and Sam Latinga (pictured at right below), lead programmer for Loki, as they prepared the Linux release of Civilization: Call To Power for distribution.
Michael: Although I’m a software developer by trade, I’ve never really been much of a game player, so this is somewhat new to me. Why don’t you both give us some background information. How did you get into the world of gaming?
Scott: Well, I am not technical, but I am a game player. I came up through stints at Apple and LSI Logic and a few other places. After that, I went over to the “dark side”—law school. While working as a software licensing attorney at an accounting firm, I got involved with some game companies and was introduced to Linux. Dan Kegel at Activision introduced me to Sam.
Sam: My background is mostly in systems administration, but I’ve been interested in game system portability for a long time. I’ve worked on things like the Maelstrom port. When Scott came to me with the idea of porting games, I was a bit skeptical. When it became apparent to me that the idea was for real, my interest grew.

Figure 2.
Michael: What made you decide that now was the time to start porting games to Linux?
Scott: I first thought about games on Linux in 1998—much has happened since then. We were lucky and in the right place at the right time. When looking at Civilization, we were fairly sure we were going to lose money on it initially. Then, as I became more familiar with Linux, I heard about the GNOME and KDE projects. Knowing those sorts of familiar interfaces would be available along with the usual benefits of running on Linux convinced me a consumer market would develop for Linux and Linux products. I knew that if Red Hat could get a distribution on the shelf, I could certainly get a game there.
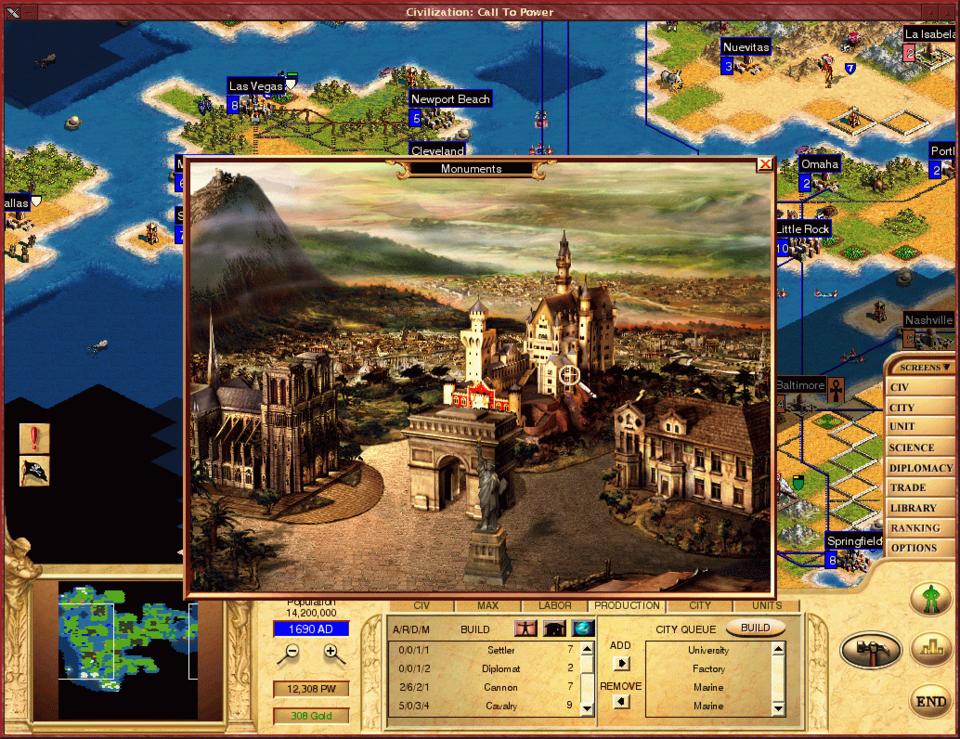
Figure 3.
Michael: The game was originally developed by Activision. Did you contact them about doing the port, or had they been looking for someone to do it? How much cajoling was involved in getting them to sign on?
Scott: I talked to many game companies, and I’m still doing so. We were actually focusing on another game when Dan Kegel suggested we look at Civilization. We did, looking at both demos and code. The more we looked at it and worked with Activision, the more we drifted away from the other game. I think Activision had the better title, and they certainly have their act together. Phillip Erwin, in the licensing department at Activision, was instrumental in getting the project completed. MicroProse, a Hasbro company and developer of the original Civilization, had to sign off on this port along with Activision. Phillip woke the President of Hasbro at midnight on December 31 in order to get the licensing signed. He’s definitely gone to bat for us.
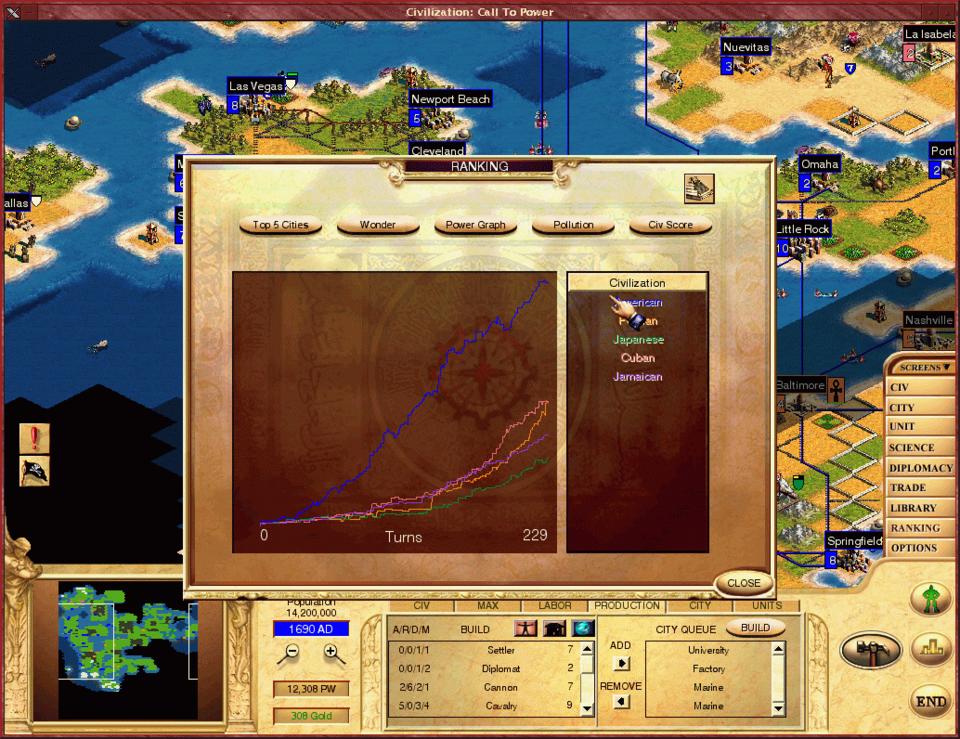
Figure 4.
Michael: Are you tied to Activision for future games, or are you free to talk with any other game producers?
Scott: We are already working on three additional titles, none of which is from Activision. Of course, I would love to do more Activision titles and we are pursuing that too.
Michael: Is this the same game as the PC version? Did the game play have to change at all in order for the Linux port to function?
Sam: Yes, it is the same game. The game play didn’t change at all. However, we did add a few minor tweaks to the user interface which we feel make it a “real” Linux game. This is a true Linux application; that is, it’s not a Windows game running under an emulator—it’s native to Linux. The installation is native to Linux. (See “Game Review”.)
Game Review
Since the game will already have been out for some time when this article reaches print, plenty of game reviews will be available on-line. C|Net’s GameCenter.com (http://www.gamecenter.com/Reviews/Item/0,6,0-2635,00.html) had one available even before the PC version hit the streets.
From a Linux perspective, what are some features and issues of importance to those who have not yet seen the game? Well, first is installation. The folks at Loki made use of a native Tk environment to provide a graphical installation of the game’s components to disk. The process is quick (as fast as it takes to unpack the massive tar file) and quite painless. I did hit a minor bug at the end of the installation, but it had no ill effects on playing the game. Sam mentioned that the bug should be fixed before the initial Linux release.
From a stability standpoint, the game played perfectly for about six hours before it died with a segmentation fault. I attribute this to a somewhat less than optimal system configuration of 64MB memory (which had to tackle the game, Netscape and about a dozen other X applications at the same time). In general, the game doesn’t seem to have many run-time problems. In all cases, the game does seem to catch the problem, since the messages (directed to standard out, i.e., the console from where the game was started) are not quite the typical core-dump messages.
There are some annoying playing features, which are not part of the Loki port but an aspect of the original game design. For example, the game will automatically select a “unit” (one of the people or cities you control) at times, especially after you just clicked on another one. On slower systems (like mine), mouse clicks can be queued up, so when this automatic unit switch occurs, you accidently cause that newly (and unwanted) selected unit to move to an unexpected location.
The game played well, although a tad slow at times (system: 200MHz Cyrix with 64MB). In a few places, the dialog boxes wouldn’t go away or were not redrawn correctly after an expose event (e.g., playing a movie). I had to guess where the Close button was on some of those boxes. This happened only while playing the tutorial game. In a normal game, these problems didn’t show up.
It was also not clear how to remove some of the message boxes along the left side of the screen. Some seem to go away after the end of a turn, but others stick around seemingly forever. This means the boxes stack up over time, although the game handles a large number of these fairly well, giving an arrow box to see overflow entries. Again, this problem showed up only during the tutorial game, which I played long after the tutorial ended. When I switched to a new game, this problem went away completely, even after an extremely long play with a moderately advanced civilization. All the icons on the left side of the screen during normal (non-tutorial) game play were removed either at the end of a turn or when I clicked on the “eye” icon to address the issue immediately.
Other pluses for the game:
- You can lock units together to move them or to attack enemies. Apparently, this is a big improvement over the original Civilization game.
- GameCenter.com complained about bugs and crashes, but I had very few. Of course, a game crash on Linux isn’t quite as fatal as it probably was for GameCenter’s reviewers.
- GameCenter.com mentions a few weak points for the game: no autosave, uneven play balance and weak AI in some important areas. Except for autosave, I didn’t experience any of these problems. The game is a major advance over anything I’ve seen on a UNIX/Linux platform to date. I think they miss the main point—is it fun to play? Yes, it kept me glued to the system for eight straight hours! Since many Linux users may not be used to this caliber of game, they may be less critical.
- The game can be run in multiple screen resolutions under X, from 640×480 to 1600×1200 (if your system supports it). The higher resolutions work better for advanced game scenarios where you have many cities and a large area of geography to cover. Graphics in all cases are quite good and very clear. Text gets hard to read at lower resolutions, especially when you zoom out on the playing area, but that’s to be expected.
Michael: Were there any engineering limitations—libraries, for example, that you had to wait for before you could start the work?
Scott: Sam evaluated the Loki code, making sure their proprietary libraries could be either ported or emulated on Linux. The library we used is SDL, the Simple DirectMedia Layer. Sam authored SDL with an eye toward creating a cross-platform media layer for games. All the graphics and sound in the game have been ported to SDL, replacing the equivalent DirectX calls from the Windows version.
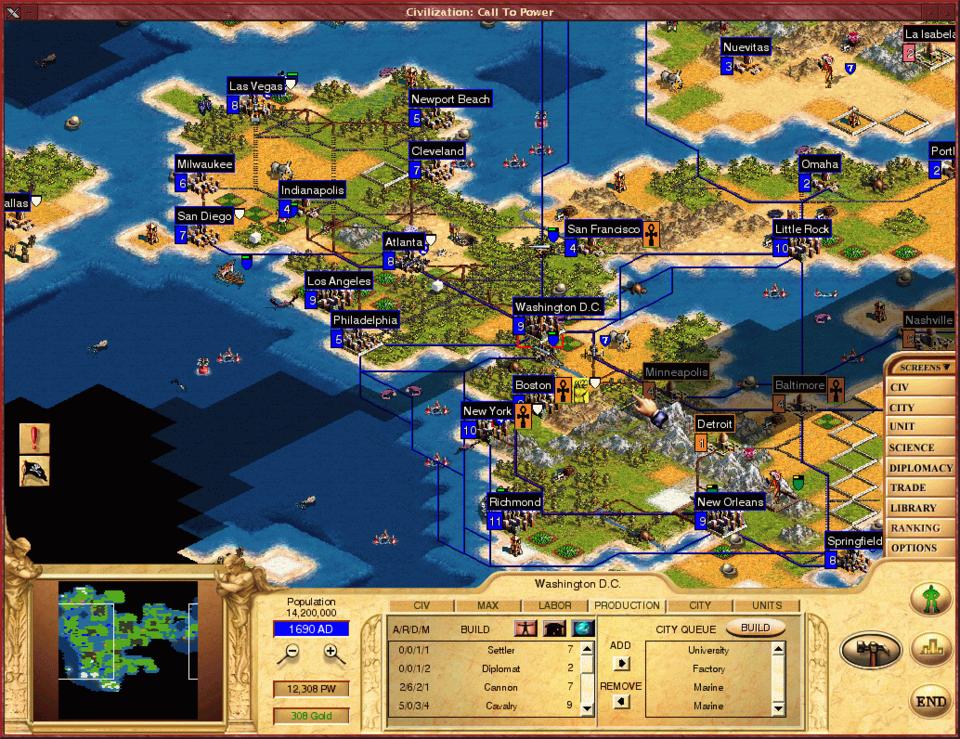
Figure 5.
Sam: The game also uses FreeType for font rendering. Activision did this on their own, which was really cool. It’s one of the things they did to make the game more portable.
Figure 6.
Michael: So you had what you needed to get going?
Sam: Basically, we had all the tools we needed from the start, with a few exceptions. None of the available off-the-shelf installers and video playback tools were adequate for our needs.
We evaluated the available open-source video playback tools, brought them in, updated them and put them into the game with our modifications. We will release the playback tool back to the Open Source community.
Figure 7.
Michael: The community will appreciate that, I’m sure. How long did it take for this first port? Will it take as long for future ports, or did you spend some time during the original port building infrastructure for the porting efforts?
Scott: We started the port in December 1998, and coding began in January 1999. It didn’t take that long—roughly four months. Part of the reason the port went so fast was the great support we received from Activision. They responded quickly to our questions and requests. With future games it may not take as long, but each game is unique. It depends on how tightly coupled the game is to the Windows API.
Gaming on Linux
Although the most professional and sophisticated of the bunch, there is a lot more to gaming on Linux than Civilization: Call To Power. Two other big-name games are the highly popular Quake series (which were the first of the really big names to make their way over to Linux) and Hopkins FBI (http://www.hopkinsfbi.com/). The latter is by MP Entertainment, a French company, and is a shoot-em-up game that uses hand-drawn animation. It is available now.
According to a contact at MP Entertainment, they are working on a new project for Linux: a “team fortress/Special Ops”-type game, with single- and multi-player (1-128 players) modes. A beta version of the game will be on-line in October and they expect to release the final version sometime in January 2000.
They are also working on Hopkins FBI 2, but they don’t know if it will be ported to Linux yet. They are awaiting the result of the sales of Hopkins FBI for Linux.
The latest in the well-known Quake series is Quake 3 Arena—a multi-player shoot-em-up game. The test version was released for Linux in early May. It requires a 3Dfx Voodoo 2 card and the 3Dfx Linux Glide drivers. You can check out id Software’s Quake 3 Arena page at http://www.quake3arena.com/.
A few other projects designed to make running existing games on Linux easier are available. The Sarien AGI (http://homepages.ihug.com.au/~entropy/agi/) Interpreter, which allows classic Sierra titles such as the early Kings Quest games, was in early development at the time of this writing (early May). A similar project, LAGII (http://www.zip.com.au/~gsymonds/LAGII/), claims to have the ability to run several of the older Kings Quest games already.
A number of projects, including CIV:CTP, Hopkins FBI and the MpegTV Player 1.0, have used or will use the SDL package for graphics and audio. SDL, Simple DirectMedia Layer, is a portable library that runs on Linux, Solaris, Win95 and BeOS. You can find out more about this library, as well as links to other projects that have used it, at http://www.devolution.com/~slouken/projects/SDL/index.html. Sam Latinga, the main developer of the CTP project, developed SDL.
Of course, you can also get some well-known games, such as StarCraft, to run under WINE, the Windows pseudo-emulator. (It is not really an emulator, but it’s simpler just to refer to it that way.) Information on how to do this can be found in various places, but you should probably start at Linux Games (http://www.linuxgames.com/) or Linux Game Tome (http://www.happypenguin.org/news). Be warned, however, that if you’re running a high-end game like StarCraft on a Windows emulator over Linux, you will need a fairly fast system with lots of memory. Games, by their very nature, are power-hungry.
Sam: Much of the user interface was provided in the game, so that part of porting wasn’t difficult. However, in places where there was a tight tie-in to the Windows API, the port was a real pain.
Michael: I can imagine. When I got ready to install the pre-release version you sent me, I noticed that the game requires 400MB of disk space. Is it common to have such large installation requirements for games? Additionally, 43MB is a large footprint for a runtime binary from a Linux perspective. Will these sizes (installation and runtime) go down eventually?
Scott: Games are always hardware-intensive. The game binary is only 7.8MB. The rest is just as Activision designed it. Large installations (disk requirements) are common for games under Windows.
The game is designed to run from a CD, but due to space limitations on the CD, it can’t currently be run that way. The files on the CD are compressed and would have to be uncompressed on the CD to run from there. We have no release plans for a CD-based Civilization, but we are aware of the need for such features and will be looking into that possibility for future games.
Michael: Any plans for hardware-accelerated graphic support? Have you talked to any of the X server vendors (XFree, Metro or Xi Graphics) about that?
Scott: Yes. We’re talking to people on both sides—hardware and software—about hardware acceleration. We’re working on a 3-D game right now that will be hardware-accelerated.
Civilization is truly a breakout product. It is a triple-A product released hot on the heels of the Windows version going into stores. That includes SuSE in Europe and Macmillan Publishing in North America. We intend to place it in all the big stores—all the places that sell software. Wherever you see Red Hat, you’ll see our game. That’s not true for the average Linux game at this time. By doing this, we’ve shown there is a market for this game, and games in general, on Linux. Many announcements are being made by 3Dfx, Creative and other people. They are coming on board because they realize games draw hardware sales.
Civilization Playing Tips
Sam gave me these tips for the game. These aren’t “shoot the wizard twice in the butt and you get bonus points” type tips. They are configuration tips—things to make playing the game easier or more convenient.
Any tips you find for game play on the Windows version are applicable to the Linux version as well, since there are no game-play differences between the two.
- You can hit ctrl-Z at any time to minimize the game.
- If a CD-ROM is in the drive and readable, the game will try to play audio tracks from it. If the CD is mounted and the videos are not installed, the game will detect the mount path and read the videos from the CD. The game looks in the /etc/fstab directory for an entry using the iso9660 file system type for the CD-ROM device.
- Pressing caps lock will bind the mouse to the CivCTP window so scrolling works nicely. Pressing caps lock again will release the mouse.
- The middle button of a three-button mouse can be used to scroll the map by dragging it.
- CivCTP allows you to control mouse speed and CD volume using the normal system tools, and so does not need a control panel for those configuration items.
- The Linux version of CivCTP uses a text field implemented from scratch and has UNIX key bindings:
- ctrl-A: move to beginning of line.
- ctrl-E: move to end of line.
- ctrl-B: move backward.
- ctrl-F: move forward.
- ctrl-U: erase line.
- The -nocdrom command-line option prevents the game from trying to access your CD-ROM.
- Setting the environment variable CIV_FULLSCREEN to 1, then running the game as root will allow it to use the XFree86 DGA extensions and run in full-screen modes. Caution: This is an unsupported configuration and may lock up your display.
- You can set any window resolution you desire (800×600 or better) by editing ~/.civctp/userprofile.txt and changing the lines beginning with ScreenRes.
- If the pause key is not bound by the window manager, it will iconify the game.
- If the print-screen key is not bound by the window manager, it will take a screenshot of the game and dump it to ~/.civctp/screen.bmp.
- Your personal preferences and save games are saved to the ~/.civctp directory, allowing multiple users to play the game on a single machine.
- If the window manager toolbars get in the way of the game, you can use the Graphics options screen to change the size of the CivCTP window.
- If the window is the same size as the display, it will run without a title bar, but if the game runs in a different resolution, it will have a title bar.
- To prevent your cities from being converted by clerics, place walls around them (i.e., build “City Walls”).
Michael: So there will be many changes in the gaming market down the road. With all those games coming, how hard is it to do these ports? What are the biggest areas of work in porting a game from Windows to Linux? Is it on the technical side or in the business details (including things like documentation)?
Sam: From the programmer’s perspective, it’s probably 50-50.
Scott: The programmers had a few things they were doing for the very first time: compiler debugging and a few infrastructure issues. Having done that work, we can leverage it in the future. On the business side, the first time is much harder. This is the first shrink-wrapped game for Linux that can be found in Best Buy, Fry’s and CompUSA. A fair bit of work was needed just to contact game companies with both a great product in good shape for porting and an interest in exploring this market! In addition, we are working on three other products right now and that will just keep increasing. Much of our past work will carry over—it was necessary only because it was the first time.
Sam: Although each game will be unique, the business side stays more stable. It does not change much after the first game.
Scott: With Linux becoming more commercial, you have to justify your products to the free software community and to the business world. In the business world, you pay to put your product on the shelves, do co-marketing, and pay for ads, bundling and so forth. That’s a great deal of work and an important part of legitimizing the Linux platform for other games.
Michael: Scott, do you think there is room in the Linux market for more than one game-porting company at this time?
Scott: I get the occasional e-mail from someone else who wants to port games to Linux. We know we’re not going to be the only ones doing this. Several other games, not necessarily ports, are available already, for example, Hopkins FBI and Quake 3. We’ve picked our niche for now by doing top-20 games. Since so many games come out each year, it’s self-evident that we cannot port everything or even everything considered good.
We came in fairly early to prove to the computer industry, the game market and the Linux market we could do this. We wanted to position ourselves as the people who are doing the triple-A products. It’s not quick and dirty. It’s not contract programming. We’re taking the source, re-implementing it for Linux and publishing it for the Linux community.
We’re a godsend for game companies. At a time when they’re laying people off, we offer another market for games already making money for them.
Michael: Well, the game market for Linux is fairly large. But how do you find out where that market is and what they want? You mentioned in an interview with LinuxToday that you read Slashdot and LinuxToday. Do you feel these on-line Linux news sources are representative of the whole market for Linux games, or is there a larger market beyond the generally technical readers of sites like these?
Scott: There is a market right now just with current Linux users. As it grows, it will bring in more and more people, more and more diversity. Right now you can go to Slashdot and hit a good percentage of Linux users. In two or three years, that might not be the case—not because Slashdot has gotten smaller, but because the market is going to keep broadening. Right now, we focus on the technically savvy Linux market—there is a tar file on the CD, for example. On the other hand, we’re aware that non-traditional users will be coming over. The GUI installer is there, specifically for the newbies.
Sam: I did the installer and am rather proud of it, since I wrote it specifically for the newbies.
Michael: I must admit it was quite easy to use. What about getting the games in the hands of users? I noticed GameCellar.com (http://www.gamecellar.com/) has a Linux area, and CTP is the only product there currently. The typical Linux user wouldn’t look for a product here, however. Does this mean you see a different market than typical Linux users? Do you plan on selling through traditional channels (Linux Mall, LinuxBerg.com, through Red Hat or SuSE, etc.)?
Scott: A good deal of interest in Linux products is showing up in many places it hasn’t been in the past. As an experiment, Costco made Red Hat available in their stores, and it outsold Windows 98. I understand you can even buy Linux products at some Wal-Marts. These aren’t traditional UNIX/Linux outlets. We’re excited about where our games might show up. Obviously, it will be at the superstores and the game stores like Software Etc., but it will be in bookstores, too. A great synergy exists with bookstores, since they already sell Linux products. Selling our game will be an incredible add-on.
Michael: What’s next? Do you have any concrete plans for future games?
Scott: No announced titles, but we have 3-D and strategy games in the works, and we’re very close to doing an RPG (role playing game). We’re going to hit as many genres as we can, with all the best titles. You won’t see twenty RPGs, but you will see the best ones.
Michael:Seems like a good bit of work for a start-up. Do you have enough staff to work these projects in parallel?
Scott: We have enough to work two in parallel now, and we want to ramp up to three or four by the end of the year. We plan on having four to eight titles by the end of the year and doubling that next year.
Michael: Well, that’s great. Thanks for taking the time to chat with me, Scott and Sam.
After we’d finished our telephone interview, Scott, Sam and I started talking candidly about playing the game. I mentioned to them how engrossed I’d become in the game during the week after I’d received the pre-release copy sent to me to prepare for this interview. I spent several nights glued to the computer until 3AM. Perhaps it’s a good thing I live alone—where does one find a spouse who actually understands and accepts such behaviour? Sam chuckled at this. “We have an in-house joke at Loki that with games on Linux, we’re going to bring kernel development to a standstill.”
We all laughed a bit more about this possibility. I don’t actually think kernel development will slow because of such high-powered games as Civilization: Call To Power. Still, kernel developers may find they are getting fewer hours of sleep each night. I wonder—does this mean the next thing to come to Linux will be an open-source caffeine supplement?
 Linux, Linux OS, Free Linux Operating System, Linux India Linux, Linux OS,Free Linux Operating System,Linux India supports Linux users in India, Free Software on Linux OS, Linux India helps to growth Linux OS in India
Linux, Linux OS, Free Linux Operating System, Linux India Linux, Linux OS,Free Linux Operating System,Linux India supports Linux users in India, Free Software on Linux OS, Linux India helps to growth Linux OS in India