Riccardo delves into the details of apcupsd, a program for monitoring and controlling APC UPSes.
Computers, like any other kind of electronic device, are very sensitive to utility power quality. According to American Power Conversion definitions (see Table 1) power anomalies can be classified as sags (better known as brownouts), blackouts, spikes, surges and noise. These power events may damage your electronic equipment, or cause loss of data if allowed to pass through the power supply to sensitive devices.
Table 1. Power Anomalies
Event: sag (brownout)
Description: Short-term decrease in voltage levels
Effect: Frozen keyboards, unexpected system crashes, loss of efficiency and reduced life of electronic equipment
Event: blackout
Description: total loss of utility power
Effect: unexpected system crashes
Event: spike (impulse)
Description: instantaneous, dramatic increase in voltage levels
Effect: damage to hardware
Event: surge
Description: short-term increase in voltage levels
Effects: stress of electronic components, premature failure
Event: noise
Description: Electro-Magnetic Interference or Radio Frequency Interference may introduce distortions in utility power sine wave
Effects: data corruption
The solution for all or part of these power anomalies is to connect an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to sensitive devices. Key to the UPS’ function is a battery, used like a buffer, where power is accumulated when the utility power is normal, and released during low-voltage or blackout events. For high-voltage events, the UPS is usually equipped with filtering electronics that are capable of reducing the voltage. UPS output power is guaranteed to be sinusoidal alternating current kept within utility power specifications.
While a UPS alone can solve the immediate problem of utility power anomalies, when a blackout occurs the UPS’ battery is used continuously, and its discharge time is faster in proportion to the load applied on the UPS output. Obviously, if a blackout is long enough, the battery charge will eventually be completely exhausted and cease to deliver power to the connected devices.
If a computer is connected to an exhausted UPS, it will suffer a system crash due to lack of power, as if the utility power suffered a blackout event. To overcome this problem, most UPSes on the market today have a built-in interface to communicate their status and to receive commands from a computer. This interface has traditionally been a serial port, but UPSes are now being shipped with USB interfaces.
UPS Alerts
Because this article is about apcupsd, we will focus on American Power Conversion (APC) brand UPSes. UPSes from other manufacturers share the same general behavior but, to date, apcupsd does not communicate with non-APC UPSes.
A UPS protocol must accomplish two main tasks. The first and most important task is to asynchronously notify when power events happen. Second, and perhaps less important, is to allow the computer to query the UPS for status information.
Table 2 lists the UPS events that are sent by APC UPSes to the computer through the serial line. Looking at this table, we find that some of these events are paramount for computer integrity during utility power anomalies.
Table 2. UPS Events
Line Fail
Sent when the UPD goes on-battery, repeated every 30 seconds until low-battery condition reached. Sometimes occurs more than once in the first 30 seconds.
Return from Line Fail
UPS back on line power, only sent if a Line Fail has been sent.
Low Battery
Sent to indicate low battery, but not on SmartUPS v/s or BackUPS Pro models.
Return from Low Battery
Sent when the battery has been recharged to some level, only if a Low Battery has been sent previously.
Abnormal Condition
Sent for conditions such as “shutdown due to overload” or “shutdown due to low battery capacity”. Also occurs within 10 minutes of Turn On.
Return from Abnormal
Sent when the UPS returns from an abnormal condition where Abnormal Condition was sent, but not a Turn On. Not implemented on SmartUPS v/s or BackUPS Pro models.
About to Turn Off
Sent when the UPS is about to switch off the load. No commands are processed after this character is sent. Not implemented on SmartUPS v/s, BackUPS Pro, or third generation SmartUPS models.
Replace Battery
Sent when the UPS detects that the battery needs to be replaced. Sent every five hours until a new battery test is run or the UPS is shut off. Not implemented on SmartUPS v/s or BackUPS Pro models.
Check Alarm Register for Fault (Measure-UPS)
Sent to signal that temperature or humidity is out of set limits. Also sent when one of the contact closures changes states. Sent every two minutes, stops when the alarm conditions are reset. Only sent for alarms enabled with I. Cause of alarm may be determined by asking the UPS. Not implemented on SmartUPS v/s or BackUPS Pro.
Variable Change
Sent whenever any EEPROM variable is changed. Only supported in EEPROM on Matrix UPS and third generation SmartUPS models.
Now let’s see the most important events at work. In Figure 1, the state machine of a UPS is described in a simplified form. When the utility power is present, the UPS monitors it for failures. If a failure is detected, the UPS sends a Line Fail alert to the computer and switches itself to battery power. At this time, the computer is powered by the UPS’ battery. The UPS starts monitoring for battery power failures. If the utility power returns, the UPS sends a Return from Line Fail alert and switches back to utility power. If the battery power goes down, below a security level, the UPS sends an About to Shutdown alert and, after a defined amount of time, switches itself off.
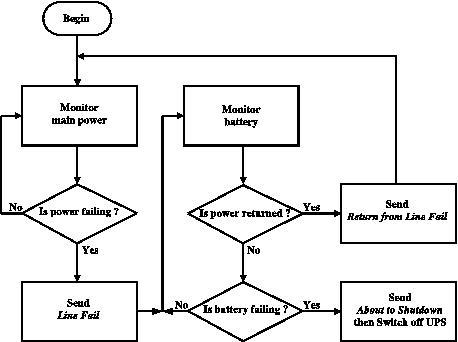
Figure 1. UPS State Machine
On the computer side, the alerts sent by the UPS are very important because they can be used to decide the actions to be executed during utility power anomalies. When the UPS switches to batteries, it could be wise to deny user logins. When the UPS is about to switch off, it is very important to shut down the computer operating system. The UPS will usually switch off after a defined delay that in some cases can even be configured, and this delay is usually long enough to allow the computer to shut down itself.
It is clear now why having an UPS does not mean, by itself, that our computer is safe. To make it really safe, the computer must constantly monitor the UPS and must be able to take actions in response to UPS alerts.
Monitoring Software: apcupsd
APC, in its catalog, offers a number of different monitoring software packages for its UPSes. Unfortunately, at the time we needed it in 1996 and 1997, no APC software for Linux was available. Nowadays there are at least four Linux products that can be downloaded from the APC ftp server including the one described here, apcupsd.
Brief History
In late 1996, Andre M. Hedrick started a Linux project called apcupsd, a dæmon whose purpose was to monitor APC UPSes for power alerts and to shut down the computer when needed. Development of this software was possible because of information gathered by the Internet, and by directly analyzing APC’s protocols.
I joined the project in October 1997 after having bought a Smart UPS v/s 650 that I still have. However, due to old age, its battery is now dead. (Many thanks to APC who gave me a new Smart UPS 1400INET, allowing me to continue development of apcupsd.)
From the beginning, apcupsd had been licensed under the GNU Public License (GPL). The GPL license was chosen because apcupsd was intended to be software for anyone, with full sources distributed without charge, and with the best support its developers were able to give.
In mid 1998, legal issues raised by APC forced Andre to remove apcupsd from its public place and distribute it as a binary-only package, removing the GPL license from its source code. This caused a lot of discussion in the Internet community during the following year.
On April 7, 1999, APC withdrew its legal objections and started actively helping our team. This allowed apcupsd to return to its original license. Nowadays, APC monitors our project on our development mailing-list and gives help on technical issues.
In September 1999, Kern Sibbald joined the project. Being an experienced software developer, he quickly became one of the main apcupsd developers.
Theory of Operation
apcupsd‘s main task is to monitor the UPS status continuously, and take action based on information received from it. Of course in real life it is not so simple.
apcupsd must be run at startup time, when the operating system services are loaded: in fact, apcupsd is just another OS service. Typically, apcupsd is run as a dæmon (i.e. in the background) with root privileges, in order to be able to take the actions needed to keep the computer healthy. Usually, it is run by the system startup scripts when the system goes multiuser.
Because of its tight relationship with the OS, the source tree contains automated installation of startup and shutdown scripts. During the compilation stage the apcupsd, initialization and control scripts are customized for the local OS. Let’s see which system files are modified, and which new files are installed by apcupsd’s installation process in a SuSE Linux system.
apcupsd’s main init script file is installed in:
/sbin/init.d/apcupsd
This script is responsible for starting up apcupsd during system startup and shutting down apcupsd during system shutdown. It is also symbolically linked to these paths:
/sbin/init.d/rc2.d/K20apcupsd /sbin/init.d/rc2.d/S20apcupsd /sbin/init.d/rc3.d/K20apcupsd /sbin/init.d/rc3.d/S20apcupsd
They are present only on runlevel 2 and 3 because apcupsd is run only in multiuser runlevels; that means runlevel 2 or 3 on SuSE Linux OS.
To be able to shutdown the computer properly on power failures, apcupsd relies on its own service script located in:
/etc/apcupsd/apccontrol
and on a patched halt script. When apcupsd detects a situation that needs an emergency shutdown, it first creates two files called /etc/nologin and /etc/apcupsd/powerfail.
Then it initiates the system shutdown. apcupsd will be killed by the system during this phase. The no login file is needed to inhibit user logins during emergency, while the power-fail file is needed during system shutdown. It is used by /sbin/init.d/halt.local as shown in Listing 1. This script will be run during system shutdown after the main halt script is run. When shutting down a computer connected to a failing UPS, we must make sure that UPS power will be removed well after all processes have been killed, and the system disks have been unmounted. In order to do this, apcupsd installation modifies the halt.local file to execute the needed actions. If the power-fail file is present during a system shutdown, all processes are killed, then all the local disks are remounted read-only, and finally we send a power shutdown command to the UPS. The final effect is that, first of all, the system is put in a safe state, and only then is the UPS power is switched off.
The computer is switched off as well by lack of power, but its main switch button is left in the ON position. When utility power returns, the UPS will, after a delay to make sure the power is stable, switch on the output power, and the computer will be restarted automatically. No user intervention is needed during these operations.
Listing 1. sbin/init.d/halt.local
# Added automatically by apcupsd installation
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
if [ -f /etc/apcupsd/powerfail ]; then
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
echo "Power down detected while shutting down."
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
echo "Sending all processes the TERM signal..."
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
killall5 -15
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
# Do a fast kill
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
sleep 1
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
echo "Sending all processes the KILL signal..."
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
killall5 -9
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
echo "Remounting filesystems read-only."
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
mounts=/etc/fstab
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
test -r /proc/mounts && mounts=/proc/mounts
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
while read des fs rest; do
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
mount -v -n -o remount,ro $fs
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
done < $mounts
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
echo "Preparing UPS to power shutdown."
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
/etc/apcupsd/apccontrol killpower
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
fi
# XXX APCUPSD - DO NOT EDIT XXX
Running apcupsd
When apcupsd is run, it first initializes the serial port and tries to determine if there is a UPS connected. Once it finds a UPS, it spawns a number of child processes, each doing a specific task. This is a design decision, due to the number of things that apcupsd must do simultaneously.
The main apcupsd process creates an IPC-shared memory pool and an IPC semaphore, then forks the apcmain task, becoming a dæmon, before exiting. The job of apcmain is to fork all the other asynchronous tasks, wait for child termination, and listen for signals. It acts as a watchdog to avoid zombies or lost signals, and it does so simply by waiting with the wait() system call.
After becoming a dæmon, apcmain forks more processes depending on which configuration has been selected in the configuration file. Figure 2 shows the operations of apcupsd once started. Let’s see them in detail.
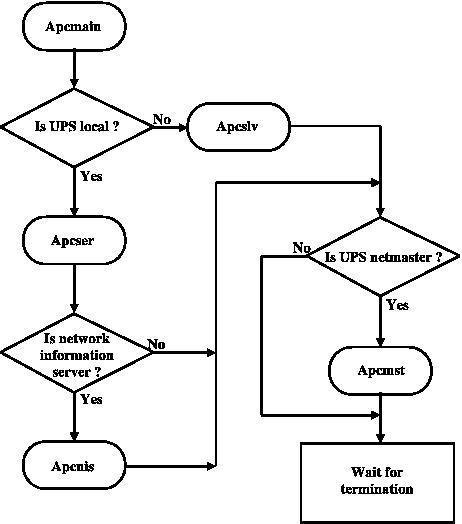
Figure 2. Startup Actions
If the UPS is local to the computer apcupsd is running on, the first task that is started is apcser. This task listens to the serial port for UPS alerts, and chats with the UPS to gather all the information needed to know the status of the UPS. In this configuration, apcser is the most important process running on the system, because, besides chatting with UPS, it executes all the actions needed to run and shut down, if necessary, the computer safely during power failures. In addition, this task generates the reports that are written to system and private log files for history purposes.
Also, if apcupsd is asked to act as a Network Information Server, it will start apcnis. apcnis is a task that accepts connections from clients on the network and delivers information gathered from the UPS to them.
If the UPS protecting local computer’s power utility is managed from a remote computer on the network, instead of starting apcser, the apcmain task will start the apcslv task. apcslv is a slave task that sits on a socket waiting for a connection from an apcupsd remote master. This process is the most important task of a networked apcupsd slave. When the network master sends the UPS’ alerts to the slave, apcslv executes the same action routine executed by apcserial. This means that a slave that receives a battery-exhausted alert from its master will shut down the computer to ensure data and hardware safety.
Finally, if the UPS is local and it powers a utility line with other slave computers connected, apcupsd will start apcmst, the master process for network alert. apcmst’s task is to send, at defined intervals, the status of the UPS to every slave configured. Also it is very important for the slaves because if the UPS sends alerts to the computer, apcmst bypasses the time-outs and reports them immediately to the slaves. In this way we can make sure that the slaves receive power alerts almost immediately.
It is interesting to note that apcupsd processes communicate with each other through IPC shared memory areas and semaphores. This means that apcupsd will not run on a computer where System V IPC or some equivalent (such as memory mapped files) is not present.
Apupsd Configuration
Before running apcupsd it is necessary to configure the dæmon to work as needed with the local hardware configuration and the desired behavior. In a standard installation, the configuration file is in
/etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.conf
This file is a plain ASCII file that contains all the configuration directives needed by apcupsd.
The directives must be properly configured before apcupsd can operate correctly. With these directives you specify the kind of cable, the model of UPS connected to the computer, the device where the UPS is connected, how to operate on power failures, logging options and much more.
Stand-Alone Configuration
A typical stand-alone configuration includes a computer and a UPS connected to its serial port.
Listing 2. Configuration File for a Stand-alone SmartUPS
## apcupsd.conf v1.1 ## # # ========= General configuration parameters ============ # # defines the type of cable that you have. UPSCABLE smart # # defines the type of UPS you have. UPSTYPE smartups # # name of your serial port DEVICE /dev/ttyS0 # # path for serial port lock file LOCKFILE /var/lock # # ===== configuration parameters used # during power failures ============= # # If during a power failure, the remaining battery # percentage (as reported by the UPS) is below or # equal to BATTERYLEVEL, # apcupsd will initiate a system shutdown. BATTERYLEVEL 5 # # If during a power failure, the remaining runtime # in minutes (as calculated internally by the UPS) # is below or equal to MINUTES, # apcupsd, will initiate a system shutdown. MINUTES 3 # # If during a power failure, the UPS has run on # batteries for TIMEOUT many seconds or longer, # apcupsd will initiate a system shutdown. # A value of 0 disables this timer. TIMEOUT 0 # # Time in seconds between annoying users to signoff # prior to system shutdown. 0 disables. ANNOY 300 # # Initial delay after power failure before warning # users to get off the system. ANNOYDELAY 60 # # The condition which determines when users are # prevented from logging in during a power failure. NOLOGON disable # #==== Configuration statements the network # information server====================== # # information server. If netstatus is on, a network # information server process will be started for # serving the STATUS and EVENT data over the network # (used by CGI programs). NETSERVER on # # port to use for sending STATUS and EVENTS data # over the network. It is not used unless NETSERVER # is on. If you change this port, you will need to # change the corresponding value in the # cgi directory and rebuild the cgi programs. SERVERPORT 7000 # # If you want the last few EVENTS to be available # over the network by the network information server, # you must define an EVENTSFILE. # Only the last 50 or so events are kept. EVENTSFILE /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.events # # ===== Configuration statements to control # apcupsd system logging ============== # # Time interval in seconds between writing the # STATUS file; 0 disables STATTIME 60 # # Location of STATUS file (written to only if # STATTIME is nonzero) STATFILE /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.status # # You probably do not want this on. LOGSTATS off # # Time interval in seconds between writing the DATA # records to the log file. 0 disables. DATATIME 0 # # ===== Configuration statements used if sharing ==== # a UPS and controlling it via the network # # normally stand-alone unless you share a UPS with # multiple machines. UPSCLASS standalone # # Unless you want to share the UPS # (power multiple machines). # this should be disable UPSMODE disable # #NETACCESS <string> [ true | false ] # Enable Network Access Support NETACCESS true
Listing 2 shows a configuration file for a stand-alone SmartUPS connected to the first serial port of the computer. On power failure, apcupsd will shut down the computer when the battery level falls below 5% of full charge or the UPS remaining run-time falls below three minutes, whichever happens first. apcupsd will send messages to user consoles every five minutes sending the first message one minute after the power failure occurs. apcupsd will not disallow user logins during a power failure. UPS events are logged in /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.events. The UPS status can be read from our CGI interface or from /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.status, which is updated every minute.
Networked Configuration
When you have a UPS that is powering more than one computer, and you want to protect every computer from power failures, you can configure apcupsd to work as network master/slave service. Listing 3 and 4 describe how to configure apcupsd as master and a slave in order to shut down both in case of a power failure.
Listing 3. Configuring apcupsd as Master
## apcupsd.conf v1.1 ## # # ========= General configuration parameters ======== # # defines the type of cable that you have. UPSCABLE smart # # defines the type of UPS you have. UPSTYPE smartups # # name of your serial port DEVICE /dev/ttyS0 # # path for serial port lock file LOCKFILE /var/lock # # === configuration parameters used during power # failures ========== # # If during a power failure, the remaining battery # percentage (as reported by the UPS) is below or # equal to BATTERYLEVEL, # apcupsd will initiate a system shutdown. BATTERYLEVEL 5 # # # If during a power failure, the remaining runtime # in minutes (as calculated internally by the UPS) # is below or equal to MINUTES, # apcupsd, will initiate a system shutdown. MINUTES 3 # # # If during a power failure, the UPS has run on # batteries for TIMEOUT many seconds or longer, # apcupsd will initiate a system shutdown. # A value of 0 disables this timer. TIMEOUT 0 # # # Time in seconds between annoying users to # signoff prior to system shutdown. 0 disables. ANNOY 300 # # Initial delay after power failure before warning # users to get off the system. ANNOYDELAY 60 # # The condition which determines when users are # prevented from # logging in during a power failure. NOLOGON disable # # ==== Configuration statements the network # information server ========= # # information server. If netstatus is on, a network # information server process will be started for # serving the STATUS and EVENT data over the network # (used by CGI programs). NETSERVER on # # port to use for sending STATUS and EVENTS data # over the network. It is not used unless NETSERVER # is on. If you change this port, # you will need to change the corresponding value # in the cgi directory and rebuild the cgi programs. SERVERPORT 7000 # # If you want the last few EVENTS to be available # over the network by the network information server, # you must define an EVENTSFILE. # Only the last 50 or so events are kept. EVENTSFILE /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.events # # ===== Configuration statements to control apcupsd # system logging ======== # # Time interval in seconds between writing the # STATUS file; 0 disables STATTIME 60 # # Location of STATUS file # (written to only if STATTIME is non-zero) STATFILE /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.status # # You probably do not want this on. LOGSTATS off # # Time interval in seconds between writing # the DATA records to # the log file. 0 disables. DATATIME 0 # # ====== Configuration statements used if sharing === # a UPS and controlling it via the network # # normally standalone unless you share a UPS with # multiple machines. UPSCLASS netmaster # # Unless you want to share the UPS # (power multiple machines). # this should be disable UPSMODE net # # NETACCESS <string> [ true | false ] # Enable Network Access Support NETACCESS true # # NETTIME <int> NETTIME 60 # # NETPORT <int> NETPORT 6666 # # SLAVE <string> SLAVE my.network.slave.com # # USERMAGIC <string> USERMAGIC some_unique_string
Listing 4.
## apcupsd.conf v1.1 ## # # ========= General configuration parameters ============ # # defines the type of cable that you have. UPSCABLE smart # # defines the type of UPS you have. UPSTYPE smartups # # name of your serial port DEVICE /dev/ttyS0 # # path for serial port lock file LOCKFILE /var/lock # # ======== configuration parameters used during power failures ========== # # If during a power failure, the remaining battery percentage # (as reported by the UPS) is below or equal to BATTERYLEVEL, # apcupsd will initiate a system shutdown. BATTERYLEVEL 5 # # # If during a power failure, the remaining runtime in minutes # (as calculated internally by the UPS) is below or equal to MINUTES, # apcupsd, will initiate a system shutdown. MINUTES 3 # # # If during a power failure, the UPS has run on batteries for TIMEOUT # many seconds or longer, apcupsd will initiate a system shutdown. # A value of 0 disables this timer. TIMEOUT 0 # # # Time in seconds between annoying users to signoff prior to # system shutdown. 0 disables. ANNOY 300 # # Initial delay after power failure before warning users to get # off the system. ANNOYDELAY 60 # # The condition which determines when users are prevented from # logging in during a power failure. NOLOGON disable # # ==== Configuration statements the network information server ========= # # information server. If netstatus is on, a network information # server process will be started for serving the STATUS and # EVENT data over the network (used by CGI programs). NETSERVER on # # port to use for sending STATUS and EVENTS data over # the network. # It is not used unless NETSERVER is on. If you change this port, # you will need to change the corresponding value in the cgi directory # and rebuild the cgi programs. SERVERPORT 7000 # # If you want the last few EVENTS to be available over the network # by the network information server, you must define an EVENTSFILE. # Only the last 50 or so events are kept. EVENTSFILE /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.events # # ===== Configuration statements to control apcupsd system logging ======== # # Time interval in seconds between writing the STATUS file; 0 disables STATTIME 60 # # Location of STATUS file (written to only if STATTIME is non-zero) STATFILE /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.status # # You probably do not want this on. LOGSTATS off # # Time interval in seconds between writing the DATA records to # the log file. 0 disables. DATATIME 0 # # ========== Configuration statements used if sharing ============= # a UPS and controlling it via the network # # normally standalone unless you share a UPS with multiple machines. UPSCLASS netslave # # Unless you want to share the UPS (power multiple machines). # this should be disable UPSMODE net # #NETACCESS <string> [ true | false ] Enable Network Access Support NETACCESS true # # NETTIME <int> NETTIME 60 # # NETPORT <int> NETPORT 6666 # # MASTER <string> MASTER my.network.master.com # # USERMAGIC <string> USERMAGIC some_unique_string
The master apcupsd is configured as described above in stand-alone configuration, with the exception that the configuration directive NETACCESS is now true and the master will use port 6666 to communicate with slaves. The apcupsd master will connect to the slave at my.network.slave.com in order to communicate alerts and power events. The slave apcupsd shares the same configuration except that instead of using the serial port, it will listen to my.network.master.com to get all the information needed to operate correctly.
Advanced Configuration
apcupsd configuration is very flexible. But adding to this flexibility, you can also configure your control scripts to execute customized actions, and you can even configure your UPS eeprom to suit your needs.
Customizing apcupsd Actions
When apcupsd detects anomalies from your UPS device, it will make some decisions that usually result in one or more calls to the script located in /etc/apcupsd/apccontrol. The apccontrol file is a shell script that takes the first argument that apcupsd passes to it to do actions. These actions are set up by default to sane behavior for all possible situations apcupsd is likely to detect from the UPS. Nevertheless, you can change the apccontrol behavior for every action. To do so, simply create a file with the same name as the action you want to customize, which is passed as the first argument (argv[1], or $1 for shell scripts). Place your script in the /etc/apcupsd/ directory. The arguments that apccontrol can recognize are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Arguments apccontrol Recognizes
Keyword—Default Action
powerout — `wall’ a message telling `There are power problems’.
onbattery — `wall’ a message telling `System is on battery’.
failing — `wall’ a message telling `Battery power is failing’.
timeout — `wall’ a message telling `Timeout on Battery reached’.
loadlimit — `wall’ a message telling `Battery load limit reached’.
runlimit — `wall’ a message telling `Battery runtime limit reached’.
doreboot — Begins the `shutdown–r’ sequence.
doshutdown — Begins the `shutdown–h’ sequence.
mainsback — Attempt to cancel a running `shutdown’ sequence.
annoyme — `wall’ a message telling `Power problems, logoff now’.
emergency — Begins an emergency `shutdown’ sequence.
changeme — `wall’ a message telling `Battery failed, change them now’.
remotedown — Begins the `shutdown’ sequence, called from remote.
restartme — Attempt to restart the apcupsd.
Listing 5. /ect/apcupsd/onbattery
#!/bin/sh # # This shell script if placed in /etc/apcupsd # will be called by /etc/apcupsd/apccontrol when the UPS # goes on batteries. We send an e-mail message to root # to notify him. # SYSADMIN=root MAIL="bin/mail" HOSTNAME=`hostname` # echo "HOSTNAME Power Failure" >/tmp/$$ echo " " >>/tmp/$$ /sbin/apcaccess status 2>>/tmp/$$ cat /tmp/$$ | $MAIL -s "HOSTNAME Power Failure !!!" $SYSADMIN exit 0
If, for example, you want to write your own routine for the on-battery action, you can write your own shell script, as shown in Listing 5, called onbattery and put it in the /etc/apcupsd/ directory. Doing so will run the customized script before the default action. In case you don’t want the default action to be taken, terminate your customized script with an exit code of 99. If you want to write customized scripts to replace the default behavior, you are encouraged to edit the apccontrol script and at least mimic its behavior in your own script. Please be aware that writing faulty scripts may cause your system to crash during power failures.
Configuring the UPS eeprom
In SmartUPSes there are at least 12 different values stored in the eeprom that determine how the UPS reacts to various conditions such as high line voltage, low line voltage, power down grace periods, etc.
In general, for the moment, it is not recommended to change eeprom values unless absolutely necessary. There have been several reported cases of problems setting the Low Transfer Voltage. Consequently, if at all possible, do not attempt to change this value.
If, despite these warnings, eeprom vales must be changed, we recommend to connect your UPS to a Windows machine running PowerChute and making the changes.
In the absence of alternatives, eeprom values can be changed also with apcupsd. Before doing so, it is recommended that you make a printed copy of UPS parameters as they are before any eeprom changes, so that they can be checked against the changes made. This can be done by printing a copy of the output from apcaccess status and also of the output from apcaccess eprom.
Once this is done, choose which eeprom values you want to change. Choose the new values from the list provided by apcaccess eprom. For the battery date, and the UPS name, you can use any eight characters.
To make the eeprom changes with apcupsd you must first stop the apcupsd dæmon. See “Stopping Apcupsd” in the appropriate section of apcupsd manual. Then edit the appropriate configuration directive in /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.conf.
It is recommended to change one eeprom value at a time, by defining only one configuration directive at a time. After each change, check that everything is okay before proceeding to the next value you wish to change.
To actually change the eeprom, as root with the apcupsd dæmon stopped, enter:
apcupsd -c
When it has completed the reprogramming of the eeprom, it will print the new STATUS report. Check that you got the expected results before continuing.
Apcupsd Security Issues
apcupsd runs as root. This needs to be considered when installing the software. It needs access to the serial port, System V IPC services and the shutdown program.
If you have switched on the NETSERVER directive in your apcupsd.conf file, be aware that anyone on the network can read the status of your UPS. This may or may not be a problem. If you don’t consider this information privileged, there is little risk. In addition, if you have a firewall between your servers and the Internet, intruders will not have access to your UPS information. Additionally, you can restrict access to your apcupsd server by using the INETD services and using access control lists with a TCP wrapper.
If you are running master/slave networking, with a single UPS powering multiple machines, be aware that it is possible for someone to simulate the master and send a shutdown request to all of your slaves. The slaves do check that the network address of the machine claiming to be the master is the same as the address returned by DNS corresponding to the name of the master as specified in your configuration file.
apcupsd’s Clients
To ease UPS monitoring, apcupsd offers quite a lot of client facilities. We have already seen apcaccess, the output of which can be seen in Listing 6. apcaccess is the main client tool for monitoring UPS status.
Listing 6. Output of “apcassess status”
APC : 001,048,1088 DATE : Fri Dec 03 16:49:24 EST 1999 HOSTNAME : daughter RELEASE : 3.7.2 CABLE : APC Cable 940-0024C MODEL : APC Smart-UPS 600 UPSMODE : Stand-alone UPSNAME : SU600 LINEV : 122.1 Volts MAXLINEV : 123.3 Volts MINLINEV : 122.1 Volts LINEFREQ : 60.0 Hz OUTPUTV : 122.1 Volts LOADPCT : 32.7 Percent Load Capacity BATTV : 26.6 Volts BCHARGE : 095.0 Percent MBATTCHG : 15 Percent TIMELEFT : 19.0 Minutes MINTIMEL : 3 Minutes SENSE : Medium DWAKE : 000 Seconds DSHUTD : 020 Seconds LOTRANS : 106.0 Volts HITRANS : 129.0 Volts RETPCT : 010.0 Percent STATFLAG : 0x08 Status Flag STATUS : ONLINE ITEMP : 34.6 C Internal ALARMDEL : Low Battery LASTXFER : Unacceptable Utility Voltage Change SELFTEST : NO STESTI : 336 DLOWBATT : 05 Minutes DIPSW : 0x00 Dip Switch REG1 : N/A REG2 : N/A REG3 : 0x00 Register 3 MANDATE : 03/30/95 SERIALNO : 13035861 BATTDATE : 05/05/98 NOMOUTV : 115.0 NOMBATTV : 24.0 HUMIDITY : N/A AMBTEMP : N/A EXTBATTS : N/A BADBATTS : N/A FIRMWARE : N/A APCMODEL : 6TD END APC : Fri Dec 03 16:49:25 EST 1999
Another console-based client is powerflute that can be used to monitor the UPS status continuously as seen in Figure 3.
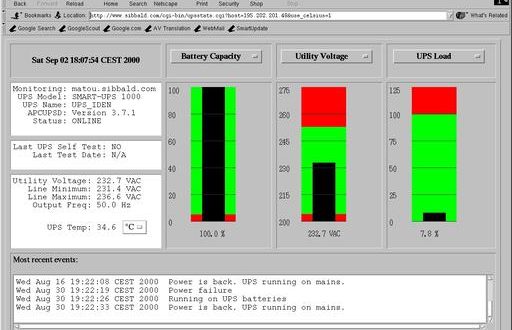
In Figure 4 another useful client for networked apcupsd is shown. It is the CGI interface that was integrated into apcupse and enhanced by Kern. If you want to be able to view UPS status from the Web, this is the best choice. Figure 5 shows the status of the UPSes connected to Kern’s main server (www.sibbald.com/cgi-bin/multimon.cgi).
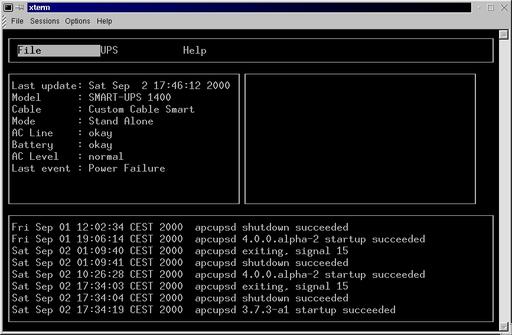
Figure 3. Powerflute
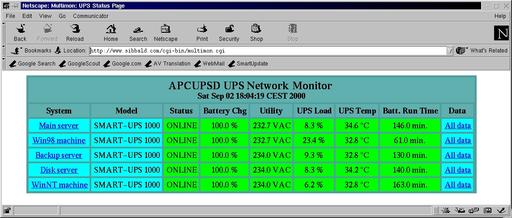
Figure 4. CGI Interface: Overview
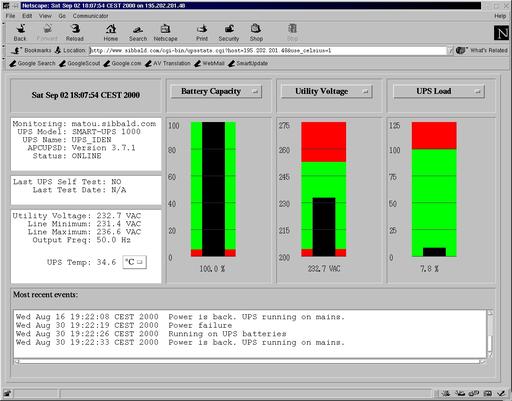
Figure 5. CGI Interface: Details on One Host
apcupsd is being ported to Win32 (9x and NT) by Kern. At the time of writing, Kern had produced a beta version of apcupsd for Windows. In Figures 6 and 7 apcupsd for Win32 status client is shown.
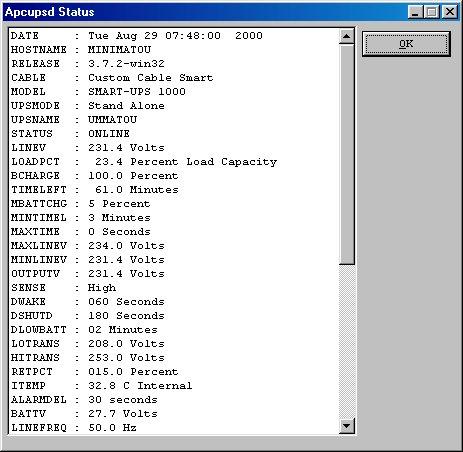
Figure 6. apcuspd for Win32
Figure 7. acpuspd for Win32
What’s Next
apcupsd is still growing. The next version of apcupsd will be a major version change and it will contain the following new main features:
- Multiple UPS control apcupsd will be able to control more than one UPS connected to the same computer.
- Network code rewrite apcupsd will be a true network dæmon with strong security features integrated into the code.
- Complete Win32 support.
- Ability to perform UPS tests from within client programs.
- If time permits, another feature, that now is more a dream rather than a development target, is to support other manufacturer’s UPSes.
 Linux, Linux OS, Free Linux Operating System, Linux India Linux, Linux OS,Free Linux Operating System,Linux India supports Linux users in India, Free Software on Linux OS, Linux India helps to growth Linux OS in India
Linux, Linux OS, Free Linux Operating System, Linux India Linux, Linux OS,Free Linux Operating System,Linux India supports Linux users in India, Free Software on Linux OS, Linux India helps to growth Linux OS in India